Pretty JSON objects to the code field
It's common to have JSON objects stored in your database. So you might want to display them nicely on your resource page.
field :meta, as: :code, language: 'javascript'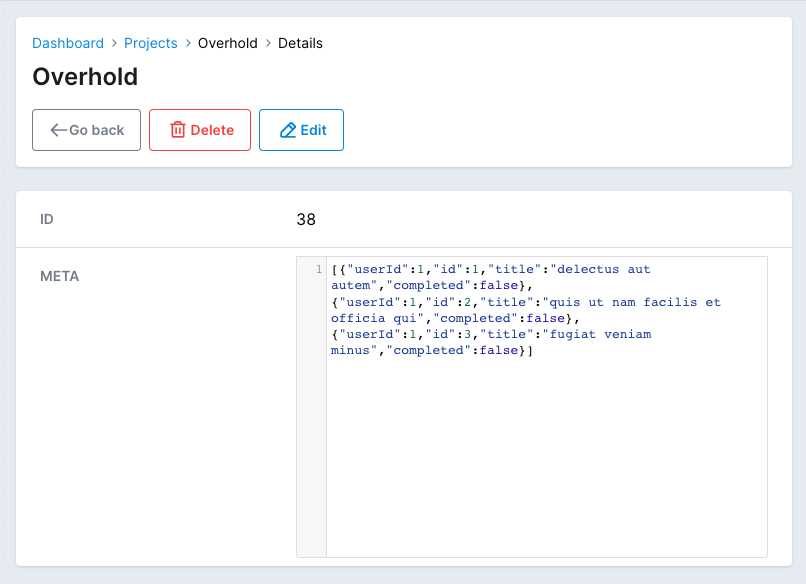
But that will be hard to read on one line like that. So we need to format it.
Luckily we can use JSON.pretty_generate for that and a computed field.
field :meta, as: :code, language: 'javascript' do
if record.meta.present?
JSON.pretty_generate(record.meta.as_json)
end
end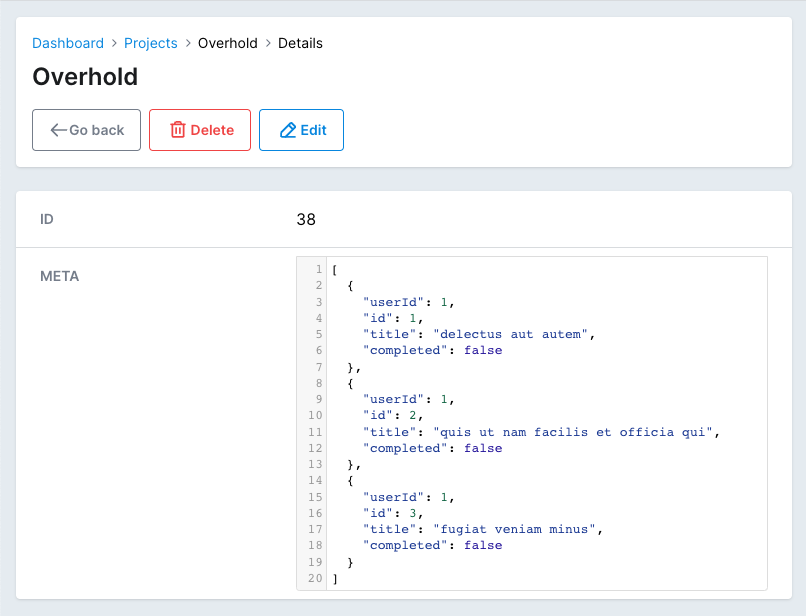
That's better! You'll notice that the field is missing on the Edit view. That's normal for a computed field to be hidden on Edit. To fix that, we should add another one just for editing.
field :meta, as: :code, language: 'javascript', only_on: :edit
field :meta, as: :code, language: 'javascript' do
if record.meta.present?
JSON.pretty_generate(record.meta.as_json)
end
endNow you have a beautifully formatted JSON object in a code editor.
When you have more JSON fields
We can use a DRY solution that will help us to make our code cleaner and readable.
1. Concern
We will create a new concern in app/models/concerns/avo_json_fields.rb to be used in our models.
module AvoJsonFields
extend ActiveSupport::Concern
class_methods do
def avo_json_fields(*fields)
fields.each do |field|
define_method "#{field}_json" do
JSON.pretty_generate(send(field).as_json)
end
define_method "#{field}_json=" do |value|
begin
send("#{field}=", JSON.parse(value))
rescue JSON::ParserError => e
# handle or ignore it
end
end
end
end
end
endThe AvoJsonFields prepares two methods for each field we provide. The first is for displaying, and the second is for storing the JSON object.
We can use it only on the models we need or include it in the ApplicationRecord for all.
class ApplicationRecord < ActiveRecord::Base
primary_abstract_class
include AvoJsonFields
end2. Usage in models
When we have the concern in place, we can use it. For the example above, it could look like this:
class Page < ApplicationRecord
avo_json_fields :meta
endThat will create two methods for the meta field: meta_json and meta_json=(value).
3. Usage in Avo resources
Now, we can use the meta_json field in our Avo resources. With the name option, we set the original name back.
field :meta_json, as: :code, name: :meta, only_on: %i[show new edit], language: "javascript" Friendly.rb - Your friendly European Ruby Conference
Friendly.rb - Your friendly European Ruby Conference