Belongs to
field :user, as: :belongs_toYou will see three field types when you add a BelongsTo association to a model.
Options
-> searchable
Turns the attach field/modal from a select input to a searchable experience
class Avo::Resources::CourseLink < Avo::BaseResource
def fields
field :links,
as: :has_many,
searchable: true
end
endWARNING
Avo uses the search feature behind the scenes, so make sure the target resource has the search_query option configured.
# app/avo/resources/course_link.rb
class Avo::Resources::CourseLink < Avo::BaseResource
self.search = {
query: -> {
query.ransack(id_eq: q, link_cont: q, m: "or").result(distinct: false)
}
}
endDefault
false
Possible values
true, false
-> allow_via_detaching
Keeps the field enabled when visiting from the parent record.
Default
false
Possible values
true, false
-> attach_scope
Scope out the records the user sees on the Attach modal.
Default
nil
Possible values
field :user,
as: :belongs_to,
attach_scope: -> { query.non_admins }Pass in a block where you attach scopes to the query object and parent object, which is the actual record where you want to assign the association. The block is executed in the ExecutionContext.
WARNING
The attach_scope will not filter the records in the listing from has_many or has_and_belongs_to_many associations. Use scope or a Pundit policy Scope for that.
field :members,
as: :belongs_to,
attach_scope: -> { query.where.not(team_id: parent.id) }In this example, in the attach_scope, we ensure that when attaching members to a team, only those who are not already members will appear in the list of options.
-> polymorphic_as
Sets the field as polymorphic with the key set on the model.
Default
nil
Possible values
A symbol, used on the belongs_to association with polymorphic: true.
WARNING
You must use this option with the types option.
Example
field :commentable, as: :belongs_to, polymorphic_as: :commentable, types: [::Post, ::Project]-> types
Sets the types the field can morph to.
Default
[]
Possible values
[Post, Project, Team]. Any array of model names.
WARNING
You must use this option with the polymorphic_as option.
Example
field :commentable, as: :belongs_to, polymorphic_as: :commentable, types: [::Post, ::Project]-> polymorphic_help
Sets the help text for the polymorphic type dropdown. Useful when you need to specify to the user why and what they need to choose as polymorphic.
Default
nil
Possible values
Any string.
-> use_resource
Sets a different resource to be used when displaying (or redirecting to) the association table.
Default
nil. When nothing is selected, Avo infers the resource type from the reflected association.
Possible values
Avo::Resources::Post, Avo::Resources::PhotoComment, or any Avo resource class.
The value can be the actual class or a string representation of that class.
# the class
Avo::Resources::Post
# the string representation of the class
"Avo::Resources::Post"-> can_create
Controls the creation link visibility on forms.
Default
true
Possible values
true, false
Since version 3.10.2, the target resource policy takes precedence over this option.
field :user, as: :belongs_to, can_create: true
In this example, even if the can_create option is set to true, if the UserPolicy responds with false to the create? method, the creation link will NOT be visible.
Overview
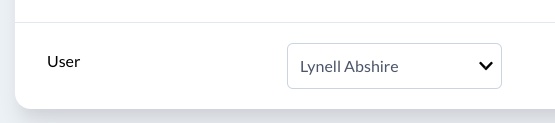
On the Index and Show views, Avo will generate a link to the associated record containing the self.title value of the target resource.


On the Edit and New views, Avo will generate a dropdown element with the available records where the user can change the associated model.
Polymorphic belongs_to
To use a polymorphic relation, you must add the polymorphic_as and types properties.
class Avo::Resources::Comment < Avo::BaseResource
self.title = :id
def fields
field :id, as: :id
field :body, as: :textarea
field :excerpt, as: :text, show_on: :index do
ActionView::Base.full_sanitizer.sanitize(record.body).truncate 60
rescue
""
end
field :commentable, as: :belongs_to, polymorphic_as: :commentable, types: [::Post, ::Project]
end
endPolymorphic help
When displaying a polymorphic association, you will see two dropdowns. One selects the polymorphic type (Post or Project), and one for choosing the actual record. You may want to give the user explicit information about those dropdowns using the polymorphic_help option for the first dropdown and help for the second.
class Avo::Resources::Comment < Avo::BaseResource
self.title = :id
def fields
field :id, as: :id
field :body, as: :textarea
field :excerpt, as: :text, show_on: :index do
ActionView::Base.full_sanitizer.sanitize(record.body).truncate 60
rescue
""
end
field :reviewable,
as: :belongs_to,
polymorphic_as: :reviewable,
types: [::Post, ::Project, ::Team],
polymorphic_help: "Choose the type of record to review",
help: "Choose the record you need."
end
end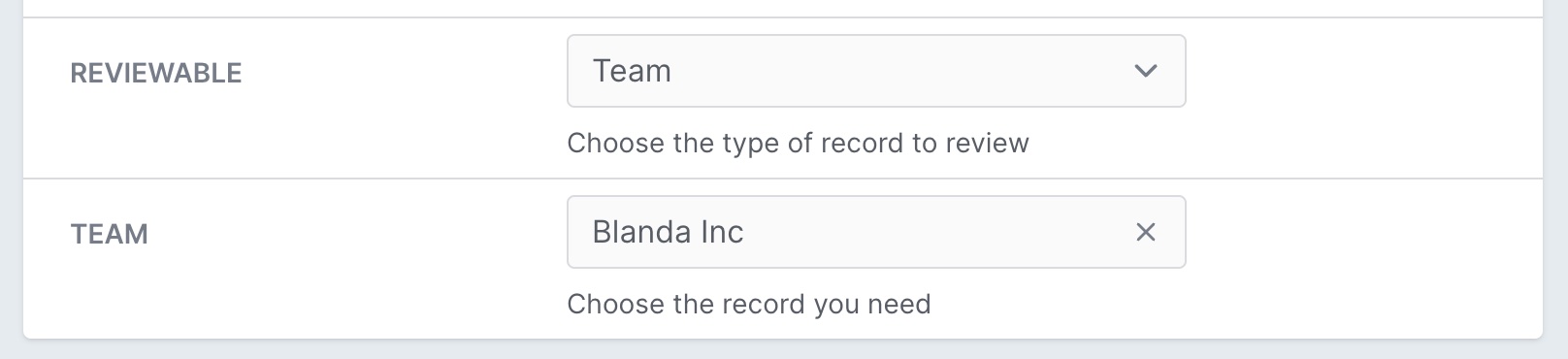
Searchable belongs_to
Watch the demo video There might be the case that you have a lot of records for the parent resource, and a simple dropdown won't cut it. This is where you can use the searchable option to get a better search experience for that resource.
class Avo::Resources::Comment < Avo::BaseResource
self.title = :id
def fields
field :id, as: :id
field :body, as: :textarea
field :user, as: :belongs_to, searchable: true
end
end
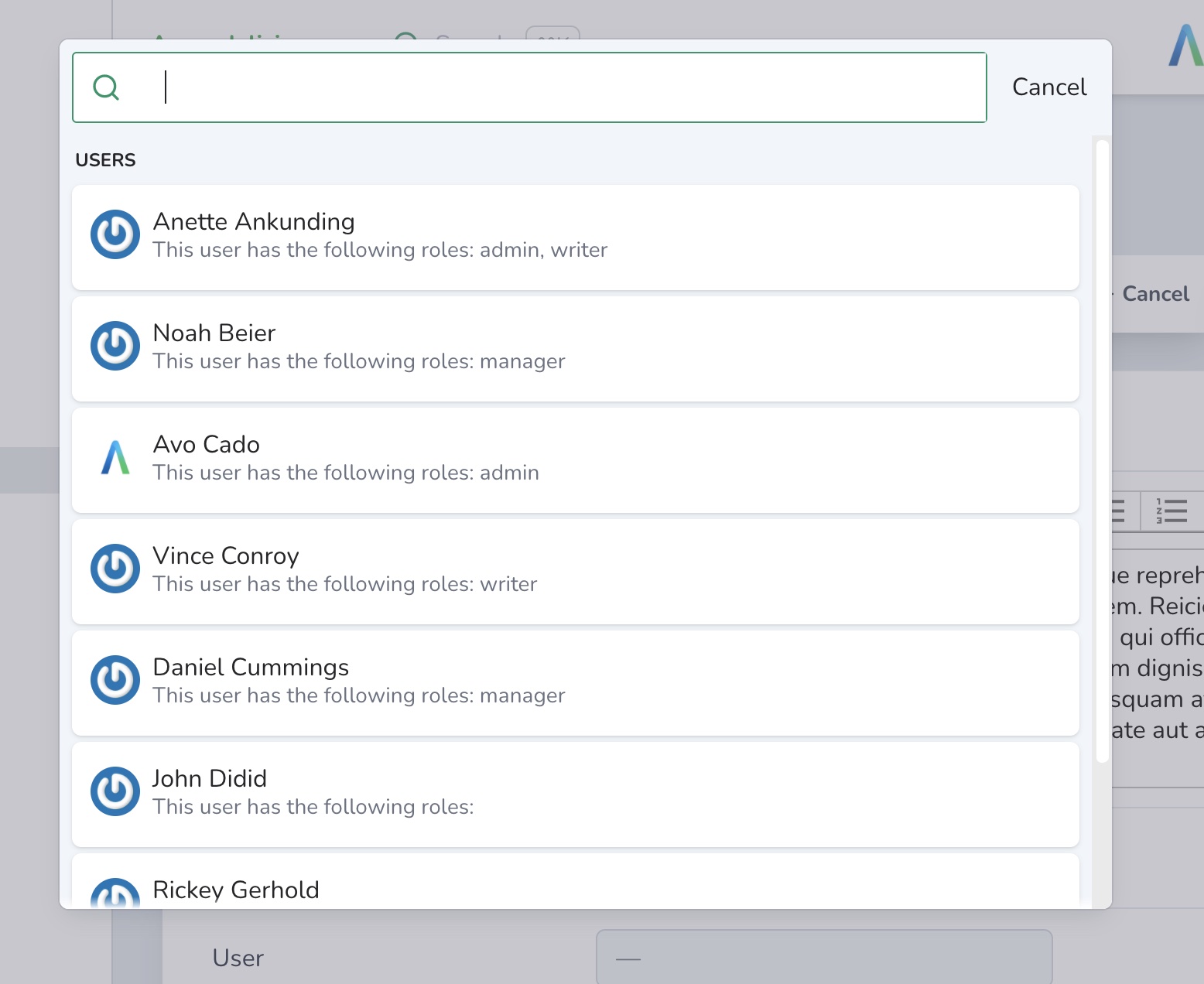
searchable works with polymorphic belongs_to associations too.
class Avo::Resources::Comment < Avo::BaseResource
self.title = :id
def fields
field :id, as: :id
field :body, as: :textarea
field :commentable, as: :belongs_to, polymorphic_as: :commentable, types: [::Post, ::Project], searchable: true
end
endINFO
Avo uses the search feature behind the scenes, so make sure the target resource has the query option configured inside the search block.
# app/avo/resources/post.rb
class Avo::Resources::Post < Avo::BaseResource
self.search = {
query: -> {
query.ransack(id_eq: q, name_cont: q, body_cont: q, m: "or").result(distinct: false)
}
}
end
# app/avo/resources/project.rb
class Avo::Resources::Project < Avo::BaseResource
self.search = {
query: -> {
query.ransack(id_eq: q, name_cont: q, country_cont: q, m: "or").result(distinct: false)
}
}
endBelongs to attach scope
Watch the demo videoWhen you edit a record that has a belongs_to association, on the edit screen, you will have a list of records from which you can choose a record to associate with.
For example, a Post belongs to a User. So on the post edit screen, you will have a dropdown (or a search field if it's searchable) with all the available users. But that's not ideal. For example, maybe you don't want to show all the users in your app but only those who are not admins.
You can use the attach_scope option to keep only the users you need in the belongs_to dropdown field.
You have access to the query that you can alter and return it and the parent object, which is the actual record where you want to assign the association (the true Post in the below example).
# app/models/user.rb
class User < ApplicationRecord
scope :non_admins, -> { where "(roles->>'admin')::boolean != true" }
end
# app/avo/resources/post.rb
class Avo::Resources::Post < Avo::BaseResource
def fields
field :user, as: :belongs_to, attach_scope: -> { query.non_admins }
end
endFor scenarios where you need to add a record associated with that resource (you create a Post through a Category), the parent is unavailable (the Post is not persisted in the database). Therefore, Avo makes the parent an instantiated object with its parent populated (a Post with the category_id populated with the parent Category from which you started the creation process) so you can better scope out the data (you know from which Category it was initiated).
Allow detaching via the association
When you visit a record through an association, that belongs_to field is disabled. There might be cases where you'd like that field not to be disabled and allow your users to change that association.
You can instruct Avo to keep that field enabled in this scenario using allow_via_detaching.
class Avo::Resources::Comment < Avo::BaseResource
self.title = :id
def fields
field :id, as: :id
field :body, as: :textarea
field :commentable,
as: :belongs_to,
polymorphic_as: :commentable,
types: [::Post, ::Project],
allow_via_detaching: true
end
end