Has Many
By default, the HasMany field is visible only on the Show view. You will see a new panel with the model's associated records below the regular fields panel.
field :projects, as: :has_manyOptions
-> searchable
Turns the attach field/modal from a select input to a searchable experience
class Avo::Resources::CourseLink < Avo::BaseResource
def fields
field :links,
as: :has_many,
searchable: true
end
endWARNING
Avo uses the resource search feature behind the scenes, so make sure the target resource has the search_query option configured.
# app/avo/resources/course_link.rb
class Avo::Resources::CourseLink < Avo::BaseResource
self.search = {
query: -> {
query.ransack(id_eq: q, link_cont: q, m: "or").result(distinct: false)
}
}
endDefault
false
Possible values
true, false
-> attach_scope
Scope out the records the user sees on the Attach modal.
Default
nil
Possible values
field :user,
as: :belongs_to,
attach_scope: -> { query.non_admins }Pass in a block where you attach scopes to the query object and parent object, which is the actual record where you want to assign the association. The block is executed in the ExecutionContext.
WARNING
The attach_scope will not filter the records in the listing from has_many or has_and_belongs_to_many associations. Use scope or a Pundit policy Scope for that.
field :members,
as: :has_many,
attach_scope: -> { query.where.not(team_id: parent.id) }In this example, in the attach_scope, we ensure that when attaching members to a team, only those who are not already members will appear in the list of options.
-> scope
Scope out the records displayed in the table.
Default
nil
Possible values
field :user,
as: :belongs_to,
scope: -> { query.approved }Pass in a block where you attach scopes to the query object. The block gets executed in the ExecutionContext.
With version 2.5.0, you'll also have access to the parent record so that you can use that to scope your associated models even better.
Starting with version 3.12, access to resource and parent_resource was additionally provided.
-> name
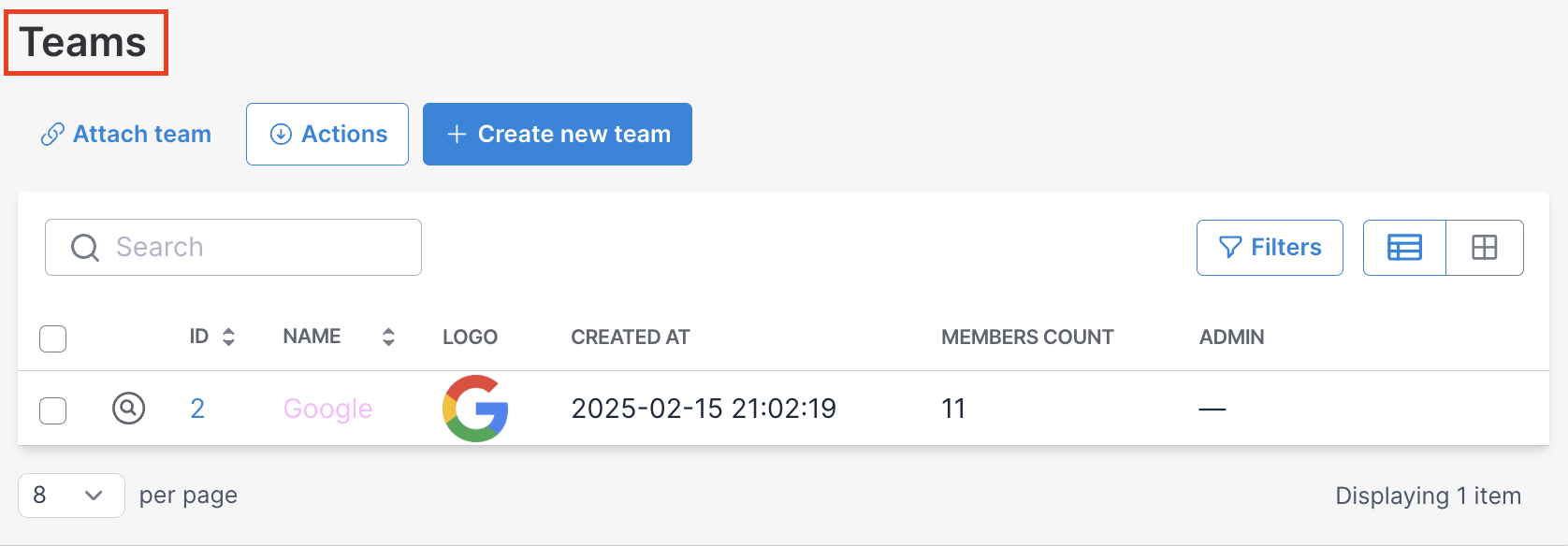
Default
Plural association name.
Possible values
Any string or any zero arity lambda function.
Within lambda, you have access to all attributes of Avo::ExecutionContext.
-> description
Changes the text displayed under the association name.
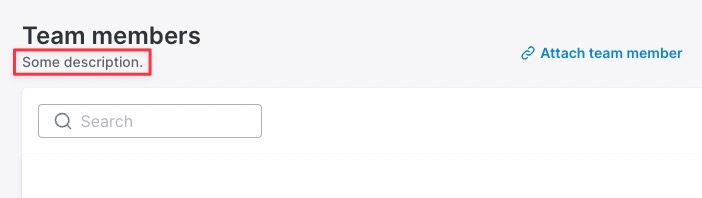
Default
nil
Possible values
Any string or any zero arity lambda function.
Within lambda, you have access to query and all attributes of Avo::ExecutionContext.
-> use_resource
Sets a different resource to be used when displaying (or redirecting to) the association table.
Default
nil. When nothing is selected, Avo infers the resource type from the reflected association.
Possible values
Avo::Resources::Post, Avo::Resources::PhotoComment, or any Avo resource class.
The value can be the actual class or a string representation of that class.
# the class
Avo::Resources::Post
# the string representation of the class
"Avo::Resources::Post"-> discreet_pagination
Hides the pagination details when only there's only one page for that association.
Default
false
Possible values
true, false
-> hide_search_input
Hides the search input displayed on the association table.
Default
false. When nothing is selected and the search_query of association's resource is configured, Avo displays the search input.
Possible values
true, false.
-> hide_filter_button
Hides the filters button displayed on the association table.
Default
false. The filters button is displayed by default and only hidden when hide_filter_button is set to true
Possible values
true, false.
-> link_to_child_resource
Sets which resource should be used in an STI scenario.
See more on this in the STI section.
Default
false. When it's false it will use the same resource.
Possible values
true, false.
Search query scope
Since v2.13If the resource used for the has_many association has the search block configured with a query, Avo will use that to scope out the search query to that association.
For example, if you have a Team model that has_many Users, now you'll be able to search through that team's users instead of all of them.
You can target that search using params[:via_association]. When the value of params[:via_association] is has_many, the search has been mad inside a has_many association.
For example, if you want to show the records in a different order, you can do this:
self.search = {
query: -> {
if params[:via_association] == 'has_many'
query.ransack(id_eq: q, m: "or").result(distinct: false).order(name: :asc)
else
query.ransack(id_eq: q, m: "or").result(distinct: false)
end
}
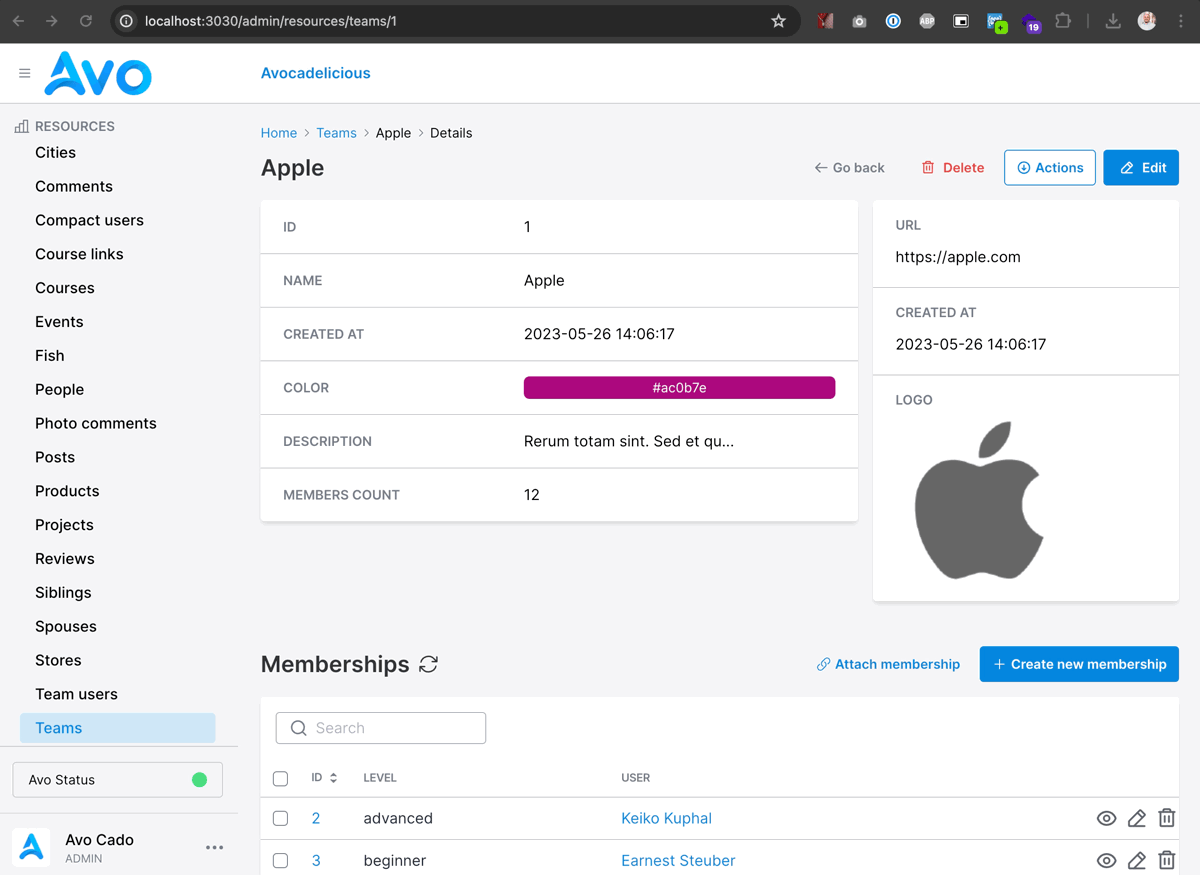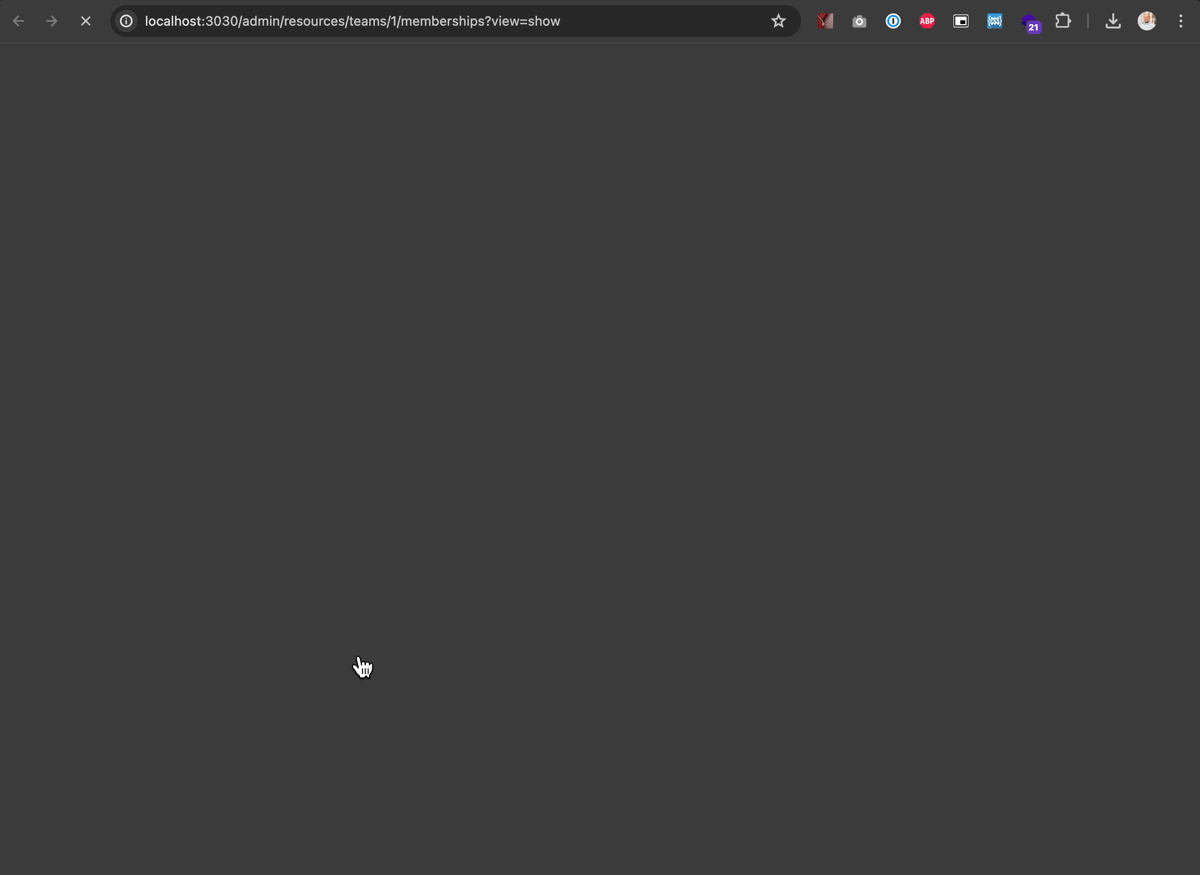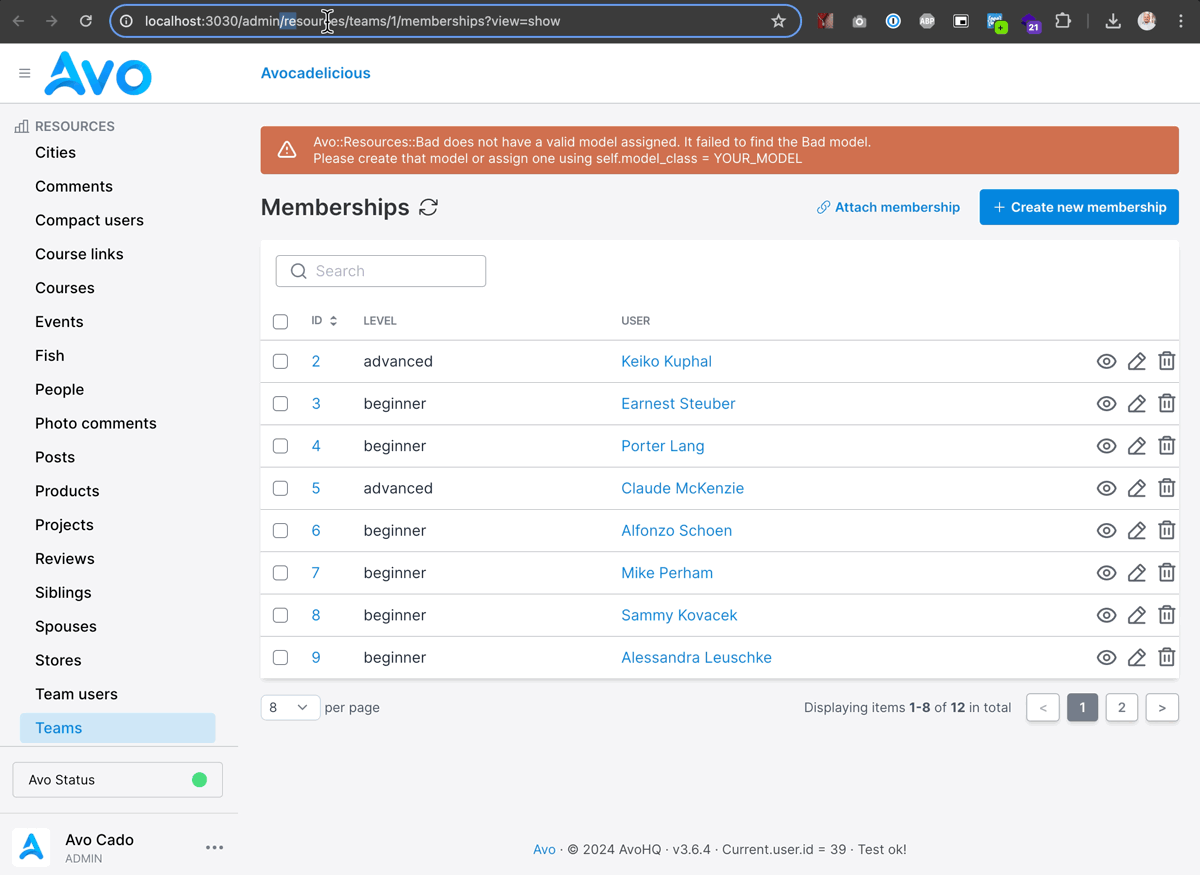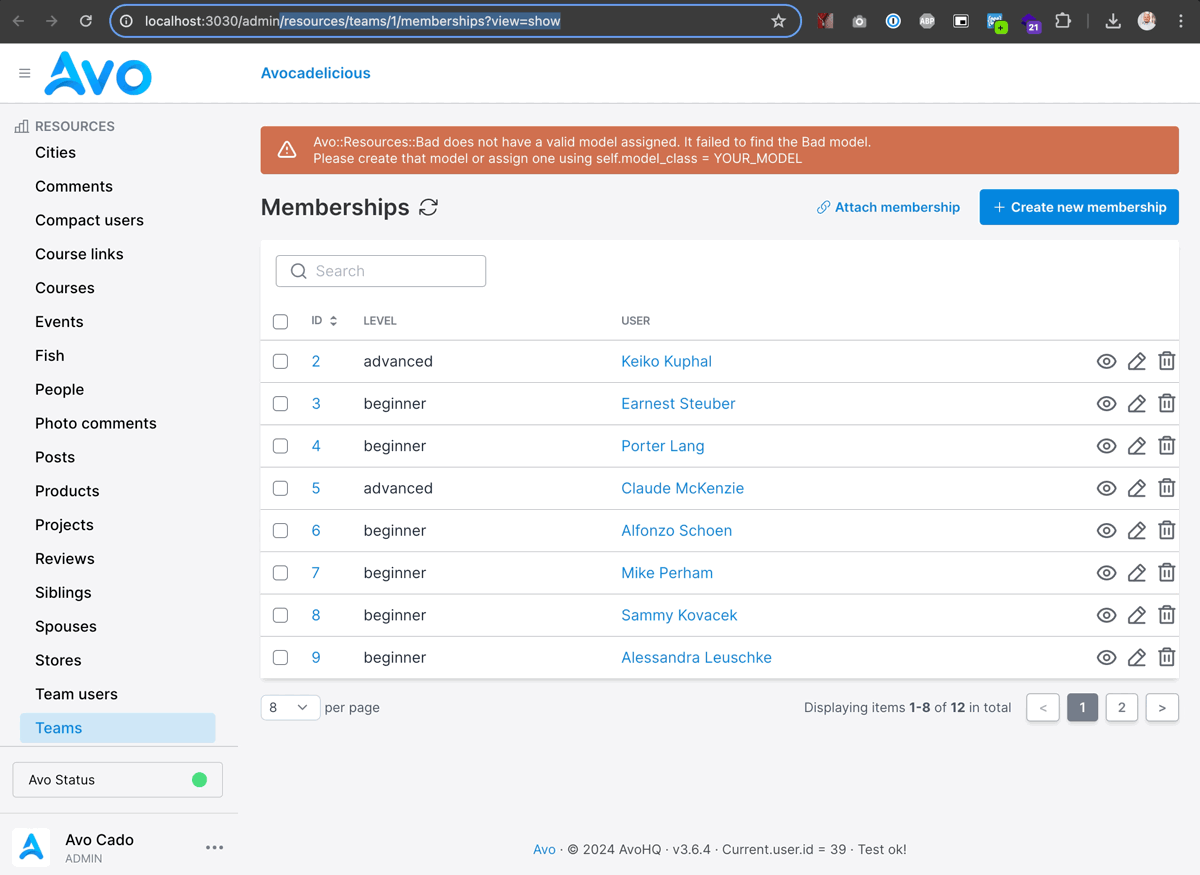
}-> linkable
You can add use this option to make the association title clickable. That link will open a new page with the same view.
This feature doesn't go deeper than this. It just helps you see the association table easier in a separate page.
Has Many Through
The HasMany association also supports the :through option.
field :members,
as: :has_many,
through: :memberships-> attach_fields
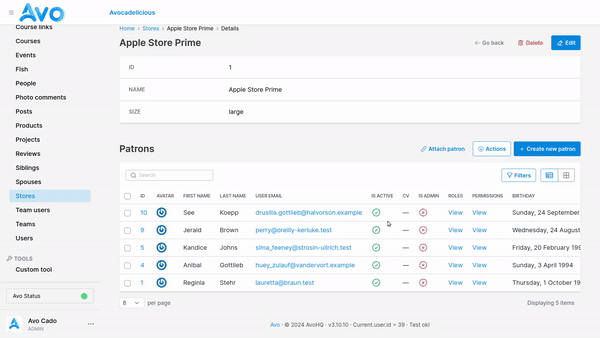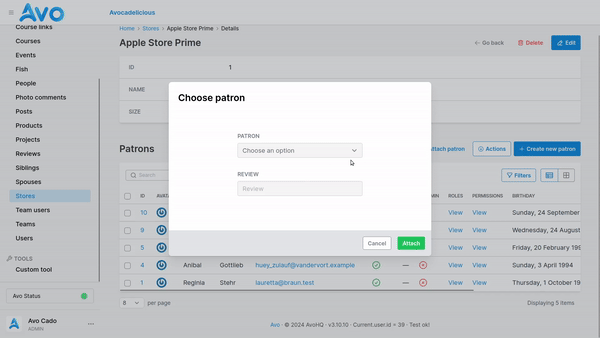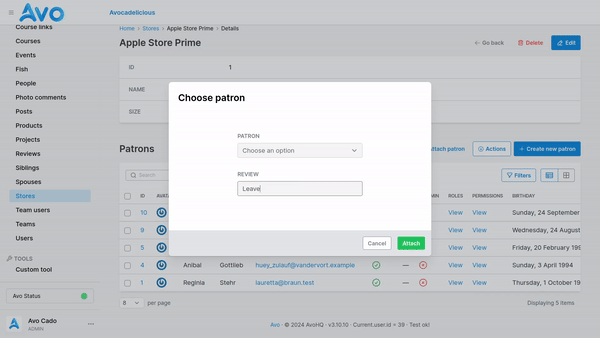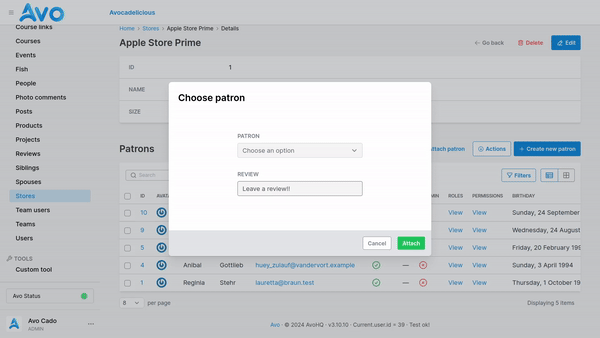
If you have extra fields defined in the through table and would like to display them when attaching use the attach_fields option.
field :patrons,
as: :has_many,
through: :patronships,
attach_fields: -> {
field :review, as: :text
}WARNING
If the through model uses polymorphism, the type must be included as a hidden field:
field :patrons,
as: :has_many,
through: :patronships,
attach_fields: -> {
field :review, as: :text
field :patronship_type, as: :hidden, default: "TheType"
}
Show on edit screens
By default, the has_many field is only visible in the show view. To make it available in the edit view as well, include the show_on: :edit option. This ensures that the has_many show view component is also rendered within the edit view.
Nested in Forms
You can use "Show on edit screens" to make the has_many field available in the edit view. However, this will render it using the show view component.
To enable nested creation for the has_many field, allowing it to be created and / or edited alongside its parent record within the same form, use the nested option which is a hash with configurable option.
Keep in mind that this will display the field’s resource as it appears in the edit view.
-> nested
Enables this field as a nested form in the specified views.
Default value
{}
Possible values
A hash with the following options:
on:Views in which to enable nesting. Accepted values:limit:(Only forhas_manyandhas_and_belongs_to_manyfields) Hides the "Add" button when the specified limit is reached.
TIP
Setting nested: true is a shortcut for nested: { on: :forms }.
Example
# app/avo/resources/book.rb
class Avo::Resources::Book < Avo::BaseResource
def fields
# Shortcut for full nesting
field :authors, as: :has_many, nested: true
# Explicit nesting on new only
field :authors, as: :has_many, nested: { on: :new }
# Explicit nesting on edit only
field :authors, as: :has_many, nested: { on: :edit }
# Explicit nesting on both new and edit
field :authors, as: :has_many, nested: { on: :forms }
# Limit nested creation (for has_many or has_and_belongs_to_many only)
field :authors,
as: :has_many,
nested: { on: [:new, :edit], limit: 2 }
end
endAdd scopes to associations
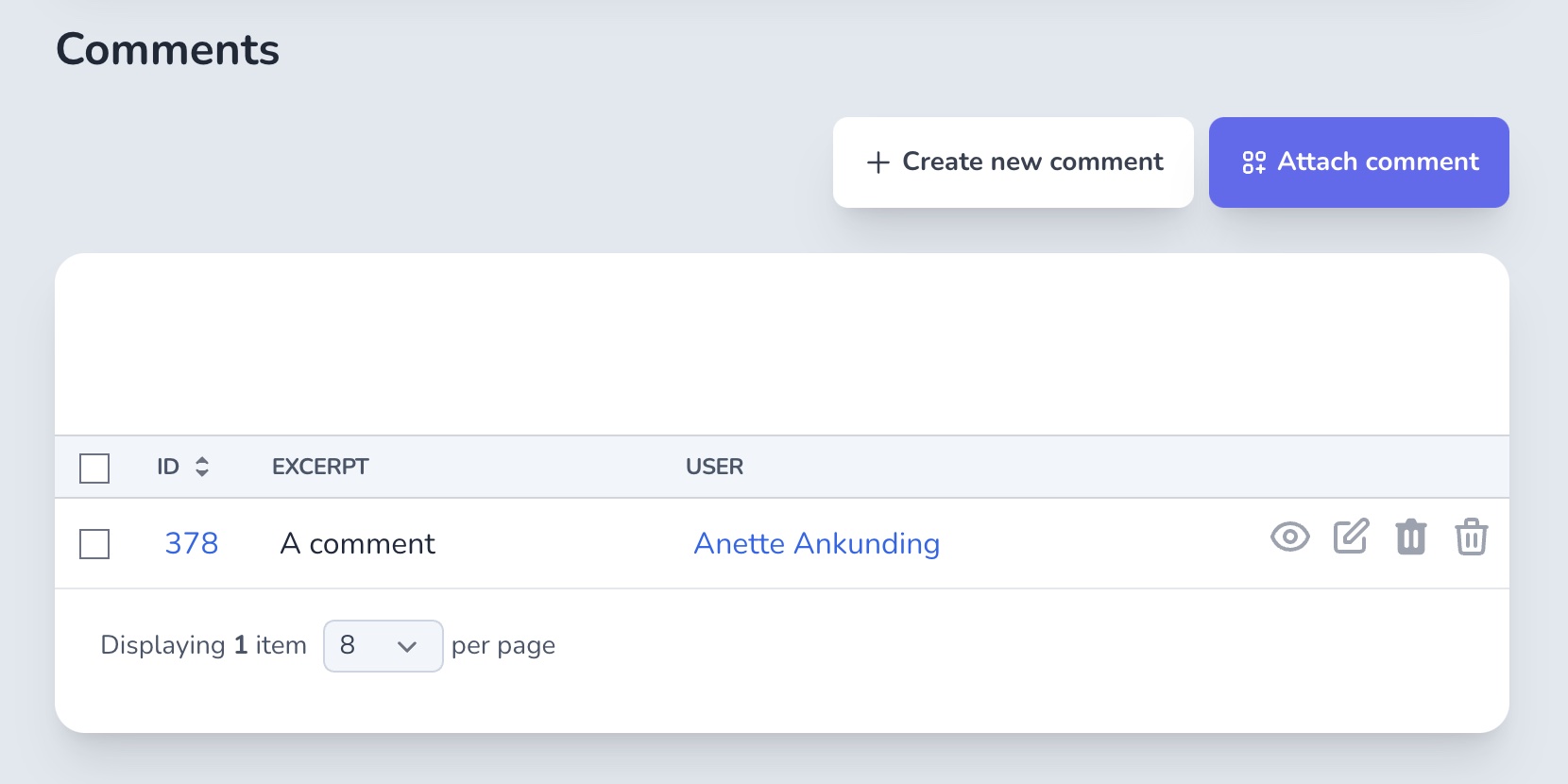
Watch the demo videoWhen displaying has_many associations, you might want to scope out some associated records. For example, a user might have multiple comments, but on the user's Show page, you don't want to display all the comments, but only the approved ones.
# app/models/comment.rb
class Comment < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user, optional: true
scope :approved, -> { where(approved: true) }
end
# app/models/user.rb
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :comments
end
# app/avo/resources/user.rb
class Avo::Resources::User < Avo::BaseResource
def fields
field :comments, as: :has_many, scope: -> { query.approved }
end
endThe comments query on the user Index page will have the approved scope attached.
With version 2.5.0, you'll also have access to the parent record so that you can use that to scope your associated models even better.
Starting with version 3.12, access to resource and parent_resource was additionally provided.
All the has_many associations have the attach_scope option available too.
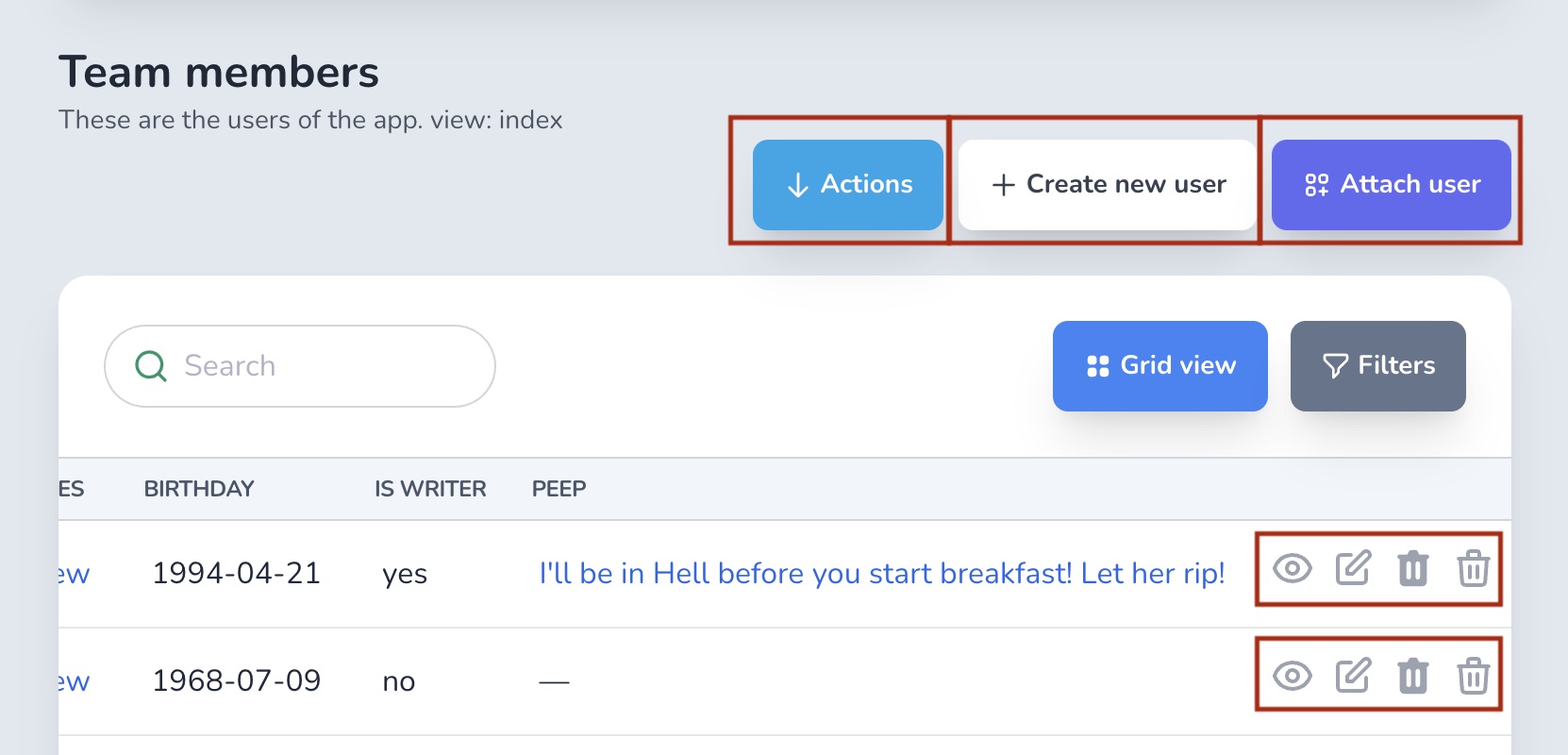
Show/hide buttons
You will want to control the visibility of the attach/detach/create/destroy/actions buttons visible throughout your app. You can use the policy methods to do that.
Find out more on the authorization page.
-> Reloadable
The reloadable option adds a reload icon next to the association title so users can easily reload just that turbo-frame instead of doing a full page reload.
Usage
To enable the reloadable feature, you have two options:
- Direct Boolean Value:
Provide a boolean value directly to the reloadable option. This sets a default behavior where the reloadable feature is either enabled or disabled based on this boolean value.
field :reviews, as: :has_many, reloadable: true- Dynamic Conditions with a Block:
For more dynamic behavior, you can provide a block to the reloadable option. Within this block, you can specify conditions under which the reloadable should be displayed.
field :reviews, as: :has_many,
reloadable: -> {
current_user.is_admin?
}In the above example, the reloadable will be visible if the current_user is an admin.
ExecutionContext
The reloadable block executes within the ExecutionContext, granting access to all default methods and attributes.

-> association
The for_attribute option allows to specify the association used for a certain field. This option make possible to define same association with different scopes and different name several times on the same resource.
Usage
field :reviews,
as: :has_many
field :special_reviews,
as: :has_many,
for_attribute: :reviews,
scope: -> { query.special_reviews }